Among all the electricity motors, industrial motors are applied in driving various kinds of industrial appliances, and generally, their powers range from 0.5 kilowatts to several thousand kilowatts. Due to diversified requirements of application, industrial motors have been categorized mainly into AC and DC motors for use in manufacturing machines, mining, electricity, HVAC, among others.
Table of Contents
ToggleDefinition
The size of the global industrial motor market will reach $98 billion by 2024 and represent more than 32% of the overall global electrical equipment market.
Considering power, in most industrial power applications, power ranges in which industrial motors often cover stretch from 0.5 kW up to thousands of kilowatts. In the context of light industry, in power, mainly from 5 to 50 kW; on the contrary, for heavy industries, it may extend to several kilowatts with 500 kW or above being required most often. For one steel plant, there could be more than 200 units of motor devices. One unit purchase cost falls between 200,000 to 500,000 yuan. Total investment could go beyond 100 million yuan.
In the last two decades, the average efficiency of industrial motors has improved by about 20%. Compared with ordinary motors in the 1990s, whose efficiency is about 75%-80%, the efficiency of high-efficiency energy-saving motors today can be as high as 92%-96%. Taking a 200 kW high-efficiency motor as an example, compared with an ordinary motor, it can save about 480 kWh of electricity every day running 24 hours, and the annual electricity saving can reach up to 170,000 yuan.
The service life of high-quality motors can reach 15 to 20 years, while that of low-quality ones may be only 5 to 10 years. A chemical company once used ordinary motors in an environment with high humidity; the service life of the equipment was less than 6 years, and the maintenance cost had accumulated to over 3 million yuan. When it replaced them with waterproof and anti-corrosion ones, the lifespan extended to 15 years and the total maintenance costs reduced by 45%.
A 100 kW industrial motor normally has a load capacity of 120%-150%, and can even withstand 200% overload pressure for short periods.
Using smart monitoring systems, factories have reduced motor failure rates by 30%, and equipment maintenance time has been reduced by 40%. Smart monitoring helps a multinational automobile manufacturer save more than 20 million yuan in annual maintenance costs.
A typical explosion-proof motor costs 2 to 3 times that of a normal motor.
The largest market for industrial motors in Asia-Pacific is globally. The market for industrial motors constitutes over 45% of total demand globally. The industrial motor market demand growth rate in China in 2023 was recorded at 8.2%. This is considerably higher than the world average of 5.6%.

Motor Types
AC motors are over 80% of the worldwide industrial motor market. More than 500 million asynchronous motors are produced every year in the whole world.
DC motors are about 15% of the global motor market. Around 30% of the production lines for automation use DC motors as their power supply.
Some small power tools may utilize motors with a power of only 500 watts, while in heavy industry, motor powers may be in the several thousand kW range. Large mining motors have powers as large as 5000 kW, and such devices often need to be run 24 hours per day without interruption.
Many new types of motors have reached IE3 or IE4, with energies all reaching above 90%. An ordinary 1000 kW high-efficiency motor can save nearly 60,000 kWh annually in comparison with traditional ones. That can save the company around 50,000 yuan in electricity costs per year. If a large quantity of high-efficiency motors are promoted in manufacturing, global energy savings will reach about $50 billion every year.
The average life span of an ordinary industrial motor is 10 to 15 years, and high-quality motors can run for 20 years or more. The annual maintenance cost of a 200 kW motor is about 5,000 to 10,000 yuan. A manufacturing company that implemented regular maintenance saw its motor failure rate decrease by about 40%, saving about 20% in annual maintenance costs.
Conventional motors are designed for 120% to 150% rated load. Motors used in power systems with transformers have much larger maximum capacity of over 200%.
The global industrial motors that require explosion-proof performance are estimated at about 15%. Explosion-proof motors can cost as much as 2-3 times compared to ordinary motors.
The factories using smart motor monitoring systems reduced failure rates by about 35%. A big mining company once installed smart sensors and reduced about 500 equipment failure incidents per year, saving more than 1 million yuan in production downtime losses.
In 2022, more than 50% of the world’s total sales of motors were made in Asia. In 2023, the industrial motor production of China reached over 400 million units, and about 30% of the motors were exported to overseas markets.
Power Types
Industrial motors can be divided into two categories: AC motors and DC motors.
About 80% of the world motor market is comprised of AC motors. Approximately 60% of the industrial motors around the globe are asynchronous motors. The common AC motor frequencies are 50Hz and 60Hz. The power supply used in most regions in China and Europe is 50Hz, whereas the US and Canada use 60Hz power supply.
A 500 kW synchronous motor has more than 97% efficiency, while the same power asynchronous motor has about 92% efficiency.
The efficiency of DC motors varies between 75% and 85%. For example, the battery life of electric tools with DC motors is 20%-30% longer than that of AC motor tools.
About 70% of small and medium-sized enterprises use AC motors.
Companies with variable frequency drive motors have enhanced their energy utilization efficiency by 15%-30%.
The market price of a 100 kW standard AC motor is about 40,000 yuan, and the price of a DC motor is usually 1.5 to 2 times that of an AC motor of the same power.
Internal Structure
The internal structure of industrial motors directly determines the performance, efficiency, and service life of motors.
A 150 kW motor can reduce the stator loss to about 10%, while motors made from low-quality materials can have losses of more than 20%.
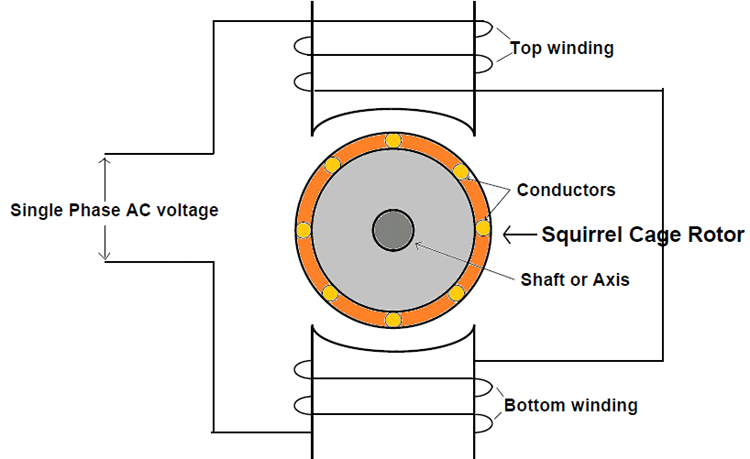
For a 100 kW squirrel-cage motor, the resistance of the rotor is generally between 0.2Ω and 0.5Ω.
High-speed motors equipped with quality ball bearings have lifetimes that could easily extend over 15 years, while in some applications using sliding bearings, their lifespan may range only 7 to 10 years. Generally, motors with a protection class of IP55 last 20% to 30% longer than those with standard casings.
The use of copper windings in a 200 kW high-efficiency motor could increase its efficiency by 5%-10%.
In the design of the excitation system, 50 kW DC motors play a very important role. Motors with electronic excitation systems can increase their power factor to more than 0.95, while the power factor for traditional DC excitation motors is usually around 0.85.
For roughly 15%-20%, energy efficiency gains are guaranteed by motors with smart control systems.
The operating efficiency and lifespan of a motor can be well ensured if the temperature rise during its operation is controlled below 100°C. For a 500 kW motor working with a water cooling system, the working temperature can be around 85°C.
Motion Output Types
There are two main types of motion output for industrial motors: rotational output and linear output.
For an industrial three-phase asynchronous motor of 200 kW, the conventional speed is 1500 RPM. In many cases where high speed is required, the motor speed could exceed 3000 RPM.
For a 50 kW linear motor, the maximum thrust could amount to 2000 Newtons. In rotating motors, the output characteristics typically depend on the speed, load, and power applied.
The performance of a linear motor is of paramount importance in applications involving higher precision control.
The automation lines driven by linear motors in the production line yield a more than 30% increase in output compared to traditional rotating motor-driven lines.
Output Power: The output power from an ordinary 500 kW AC asynchronous motor is sufficiently capable of driving most heavy machinery needs, with greater than 80% confidence in its output power.
Variable frequency drive wind power generation systems have achieved more than 15% enhancement in power generation efficiency, and the system maintenance cost is reduced by about 10%.

Different Applications
Motors provide different kinds of power output for various needs, driving mechanical equipment in industrial production, transportation, and agricultural production.
Most modern automotive production lines adopt three-phase asynchronous motors of over 100 kW for driving automated assembly robots. Using a high-efficiency motor and an auto-control system on the production line can raise production efficiency by about 30% to 50%.
The power systems of drilling platforms are generally driven by 500 kW to 1000 kW motors, and their operation efficiency is usually higher than 85%.
Pumps and fans of large-scale wastewater treatment plants are driven by 200 kW to 500 kW motors. In water pump systems, variable frequency drive technology can save up to 30% energy consumption.
The general size of motors applied to harvesters falls into the range between 100 kW and 300 kW. Newly developed motor technologies applied in farm machinery have succeeded in energy saving: 20%-30%.
2 MW wind turbines apply a synchronous motor at 400 kW. During the actual operation of a wind power plant, motors work for over 20 years. Wind power generation equipment has been installed at almost ten times higher numbers than it was 10 years ago.
As applied within the HVAC industry, industrial motors are mainly used for powering air-conditioning compressors, fans, and pumps. More than 40% of the energy supply in a typical commercial building is consumed by its HVAC system.
The general power rating for an electric bus’s electric drive system lies within the range of 150 kW to 250 kW. These systems ensure an improvement of about 40% in energy efficiency over conventional internal combustion engines.
Motor powers are normally between 1000 kW and 2000 kW for large-size electric arc furnaces. More than 20% enhancement in energy efficiency, coupled with more than 15% increase in production effectiveness, is assured by metallurgical equipment driven with high-efficient motors.
A big concrete mixer is normally equipped with 75 kW to 150 kW motor power. High-efficiency motors have been applied in concrete mixers, which save energy by about 25% during operation.
The drive motor of a modern washing machine requires a power range of 500 watts to 1 kW. Demand for motors in home appliances is increasing by roughly 5% per year.