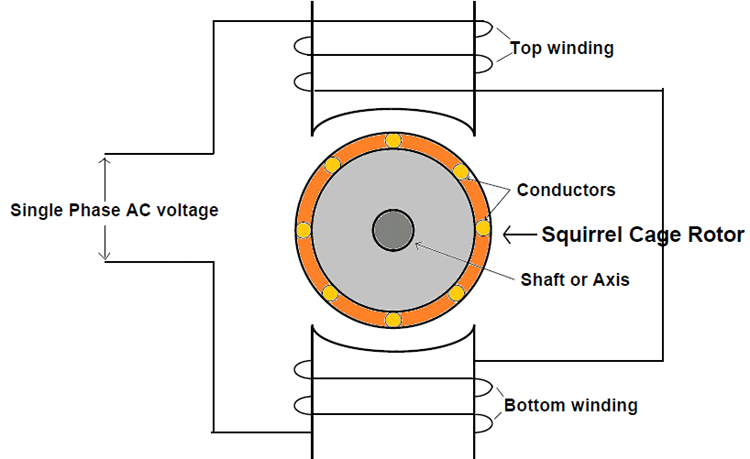
The advantages of induction motors include long life, low maintenance costs and high efficiency. The service life can reach more than 30 years, and the efficiency of high-efficiency induction motors exceeds 95%, and the annual maintenance cost is about 2%-4% of the purchase cost.
Table of Contents
ToggleSimple and reliable structure
The average life of an induction motor can reach more than 30 years, which is usually 2 to 3 times longer than other types of motors. In high-load and high-frequency application environments, induction motors perform particularly well and can operate continuously and stably without frequent failures due to wear and tear of complex internal components.
Taking a 90kW induction motor as an example, its market purchase price is usually RMB 25,000 to 30,000, while a permanent magnet synchronous motor of the same specification costs more than RMB 45,000.
Under standard load, the efficiency of induction motors is usually more than 95%, while the efficiency of traditional DC motors is generally only 85% to 90%. A factory saved about 50,000 kWh of electricity per year by replacing it with a high-efficiency induction motor, equivalent to RMB 100,000 in electricity bills.
The maintenance cycle of an induction motor is 18 to 24 months, compared with a DC motor that usually has a maintenance cycle of only 3 to 6 months, requiring more frequent replacement of brushes and cleaning of the commutator. An oil company reduced maintenance costs by more than 40% after replacing the motors on its production line with induction motors.
Because it works on the principle of electromagnetic induction, there is no direct contact between the rotor and the stator, which makes the induction motor more stable in high temperature, high humidity and flammable and explosive environments. The failure rate of induction motors in harsh environments is 35% lower than that of other types of motors.
Induction motors produce almost no sparks during use, so they can work safely in environments containing explosive gases and dust. The induction motors used in the ventilation equipment of a coal mine have been running stably for more than 10 years without any accidents caused by electrical sparks.
According to statistics from ABB, a leading global industrial automation company, induction motors have shown 99.5% reliability in industrial production, while the reliability of other types of motors is generally less than 98%. After a certain automobile manufacturer used induction motors to drive the production line, the equipment downtime was reduced by 60%, and the production efficiency was greatly improved.
The ease of use of induction motors is simple in structure, and operators can easily get started without complex training. The average fault diagnosis time for an induction motor is only 2 hours, while for other types of motors, it takes 3 to 5 hours to complete the troubleshooting and repair.
Whether in high altitude, high temperature, high humidity or high dust environment, the stability and reliability of induction motors are not affected. Most of the drive motors of wind turbines use induction motors. The equipment using induction motors has an operating life of 20% to 30% longer than other types of motors.
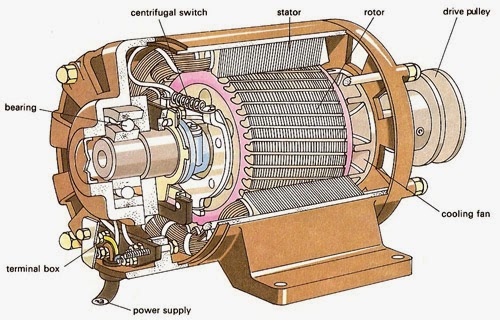
Relatively low cost
The market price of a 75kW induction motor is usually between 20,000 and 25,000 yuan, while the price of a permanent magnet synchronous motor of the same power is often as high as 30,000 yuan or more. For companies that need to purchase on a large scale, choosing an induction motor can greatly reduce the initial investment cost.
The average operating efficiency of induction motors is above 90%, especially the efficiency of high-efficiency motors can reach more than 96%. The efficiency of traditional DC motors and synchronous motors is usually only 85% to 88%. A 500kW motor runs for 5,000 hours throughout the year. With an electricity cost of 0.8 yuan per kilowatt-hour, the induction motor will save up to 200,000 yuan in electricity costs each year.
The average annual maintenance cost of an induction motor is about 2% to 4% of its purchase cost, while the annual maintenance cost of a DC motor is usually three times that of an induction motor. If the purchase cost of an induction motor is 100,000 yuan, then its annual maintenance cost is about 2,000 to 4,000 yuan, while the maintenance cost of a DC motor of the same power may reach 6,000 to 12,000 yuan.
The design and manufacturing process of induction motors is relatively simple, and the production process is relatively mature. The production cost of some standard three-phase induction motors is only 50% to 60% of that of DC motors of the same power, which makes induction motors an ideal choice for low cost and high efficiency.
The market share of induction motors in the industrial field is as high as 70% or more, especially in equipment such as fans, pumps and compressors. Induction motors are often used in conveyor belts, elevators and automation devices in industrial production lines to ensure long-term stable operation of equipment and reduce production interruptions caused by motor failures.
In oil drilling platforms and large water pump systems, induction motors can operate stably under large load changes, and their efficiency variation range is usually no more than 5%, while other types of motors may have an efficiency drop of 10% to 15% under the same load fluctuation.
According to Siemens, a global motor manufacturer, the average service life of induction motors can reach more than 30 years, and under good maintenance conditions, the service life of some types of induction motors can even be extended to 40 years. In comparison, the service life of other types of motors is generally shorter, and the service life of DC motors is generally only 15 to 20 years.
According to the European Motor Manufacturers Association, the energy-saving effect of induction motors has been significantly reflected in many industrial applications. In large water pump systems, replacing traditional motors with high-efficiency induction motors can improve the energy efficiency of the overall system by 10% to 15%, and under some extreme load conditions, the energy saving effect can even exceed 20%.
Long service life
A test conducted by the National Electric Motor Manufacturers Association or otherwise known as NEMA relates that induction motors possess an average service life of approximately 25 to 30 years. Other motors, on the other hand, such as DC motors are shorter, having a service life of about 15 to 20 years.
Another very important characteristic reflecting in both long life and low failure rate is long-term stability. Average failure rate is about 0.2%, while that of DC motors is around 0.4% and for synchronous motors with the same power it is about 0.3%.
Induction motors work on electromagnetic induction and do not have sliding contact parts, which are not easily affected by wear. For a DC motor and synchronous motor, friction easily affects the brushes, commutators, and all components placed inside. Induction motors have an average lifespan that is 30% to 40% longer than DC motors.
Induction motors have a simple construction that should be inspected periodically after every 18 to 24 months and do not often necessitate the replacement of the wear parts. However, DC motors call for the replacement of brushes every 3 to 6 months and are often sent for maintenance. Thus it saves the company’s cost on part repair and part replacement by a total of around 40% during usage of induction motors for a long duration period.
In some high-intensity industrial applications, the failure rate of induction motors in long-term operation of water pump systems is 25% lower than that of traditional motors. In some large-scale water pumping stations and sewage treatment plants, induction motors are used to drive the core equipment because they can endure long-term high-load operation without overheating or burning.
Induction motors are widely applied as drives for compressors, pumps, and other equipment on the drilling platforms for offshore oil and gas. In extreme conditions of high temperature, high humidity, and corrosion due to seawater, they can be in steady running for a relatively long time. On average, induction motors are reported to last longer by 20% to 30% compared to any other type of motor in offshore platforms.
The induction motor has sturdy housing and brushless, which can resist frequent mechanical shocks and vibration external shocks and maintain stable operations under a condition of high vibration. Only 5% failure rate of induction motors exists in an environment of high-frequency vibration, while the failure rate of other types of motors is usually 15% to 20%.
Most of the large-scale mining equipment can tolerate sudden changes in load by the induction motors without abnormal failures and shutdowns. The life of the induction motors used in the mining industry is 40% longer than for other motor types and is very closely related to the load adaptability of induction motors.
The payback period of equipment using induction motors becomes approximately 2 to 3 years shorter than that using DC motors. In addition, by saving maintenance, energy, and equipment replacement cost, induction motors can assist the company in attaining higher profitability in the long term and lower overall investment cost.
Wide range of application scenarios
The market share of induction motors in industrial equipment is over 70%, especially in pumps, fans, compressors, transportation equipment and other fields.
In the water treatment industry, induction motors are widely used to drive water pumps and sewage pump systems. Its efficiency can usually be maintained above 90%. After a large water plant adopted induction motors, its annual electricity bill expenditure was reduced by 15%, saving about 300,000 yuan.
It can withstand severe climatic conditions very efficiently in the induction motors of a wind turbine and even promises stable output when the wind speed varies drastically. The average annual failure rate is 30% lower than those involving DC motors. Its service life far exceeds 5 years more than equipment involving other types of motors.
The motor drive systems of air conditioners and ventilation equipment in commercial and industrial buildings usually employ induction motors. In modern commercial buildings, high-efficiency induction motors are used, which can lower power consumption by more than 20%. The operating cost of the system is reduced annually by about 50,000 yuan, with an overall energy efficiency improvement of 18%.
In the mining industry, for instance, failure rates of equipment which use induction motors in the same period are recorded to be 40% lower as compared to similar equipment using DC motors. Because of their ease of adaptation in harsh environments, induction motors enable continuous and effective operation under heavily dusty, damp, and scorching high temperatures, besides reducing the chances of equipment maintenance and replacement often.
In an automobile production line, the production line using induction motors will have an operating efficiency that is 20% higher than a traditional motor. Simultaneously, because an induction motor has fewer wear parts, the maintenance cost of the entire production line will be less than 30% per annum.
For example, induction motors in rail transit such as subway electric trains or even light railway systems reduce failure rates by 25% compared to other motor types. Simultaneously, vehicles’ running costs are reduced by 15%.
Induction motors can work for thousands of hours without failure in large-scale farmland irrigation systems because they are highly efficient and durable. In comparison to traditional equipment, the induction motor irrigation equipment improves the operating efficiency by 25% and cuts electricity consumption by 30%.
The service life of induction motors in the home appliance industry is about 10 to 15 years, while that of old motors is up to 5 to 8 years. Long service can thus be achieved due to induction motors without frequent repairing or replacing apparatus.
Large cold storage, refrigeration plants, and air conditioning refrigeration systems equipped with induction motors can work under very low temperatures, and the equipment service life is normally 20% to 30% longer than other motors.
Induction motors are used to power a broad range of equipment, such as mixers, dryers, and presses in food processing plants. Compared with traditional types of motors, food-processing machinery powered by induction motors increased production efficiency by 15% to 20% and were able to save up to 50,000 yuan in maintenance and electricity costs annually.

Strong durability
Failure rates of induction motors are normally lower than for any other type of motor, such as DC motors and synchronous motors, for industrial applications. The average annual failure rate of induction motors only stands at about 0.2%, while the failure rates of DC motors are 0.5% and of synchronous motors 0.4% in the same period.
Induction motors have a service life of over 30% longer than that of DC motors. In some long-running equipment, induction motors can often maintain normal operation for 20 to 30 years, while the service life of a DC motor is generally between 10 and 15 years.
Equipment in heavy industries, such as mining and steel smelting, needs to work continuously under high loads and extreme conditions. Compared with other types of motors, induction motors have a failure rate 40% lower in high-load environments; they can bear frequent fluctuations in loads without failure, greatly improving the overall stability of the equipment.
In extreme temperature environments, induction motors can operate with high efficiency in a temperature range of -30°C to +40°C, and hence are used extensively in industries such as oil extraction, chemicals, and metallurgy. DC motors and synchronous motors tend to deteriorate or fail under the same conditions.
Induction motors are versatile and have good adaptability to high humidity and high corrosion environments in working conditions with much dust, moisture, or corrosive gases. Their service life can be longer than other types of motors by 20% to 30%. This means that, while induction motors may be used in offshore oil platforms and fertilizer plants for more than 25 years, other types of motors may need to be replaced within 10 years.
Usually, in large water treatment plants, induction motors need to operate for 24 hours continuously under high load. Pump equipment with induction motors can run over 5 years without serious failure, but the failure rate of traditional motors is much higher, and parts often need to be replaced within 2 to 3 years.
Because the induction motor operates, it produces a lot of heat, which can be dissipated very quickly. The heat dissipation efficiency of induction motors is 1.5 times that of DC motors, which enables induction motors to operate stably for a long time in high-temperature environments and are not easily damaged by overheating, thus extending their service life.
In high-vibration environments such as mining and metallurgy, the mechanical vibration is more frequent. The maximum amplitude of vibration that induction motors can bear is 30% higher than that of other motors. In some large-scale mining transportation systems, induction motors can work stably for several years in an environment with frequent vibrations, while other types of motors often fail in this environment.
Some production equipment makes induction motors work under continuous overload. Induction motors can bear 120% to 150% of the rated load, while synchronous and DC motors usually can only bear 110% to 120% of the rated load.
An example is industrial equipment like fan systems where induction motors require simple checks every 6 to 12 months, whereas DC motors need brush inspections and replacements regularly every 3 to 6 months.
Brushless design is safer
In petrochemical, coal mining, and other high-risk industries, induction motors are not easy to generate sparks because they do not have brush components, thus avoiding fire or explosion accidents caused by motor failure.
When equipment using induction motors is used in explosion-hazardous areas (such as oil and gas mining or flammable gas environments), its safety is more than 50% higher than that of traditional DC motors. Since there are no brushes to generate sparks, induction motors can effectively prevent potential safety hazards.
In long-term use, the friction between the brushes and the commutator will cause wear, while induction motors can significantly reduce wear because they do not rely on brushes. The maintenance cycle of induction motors is usually 2 to 3 times longer than that of DC motors. The regular maintenance cycle of induction motors is generally 1 year, while the maintenance cycle of DC motors is usually 6 months.
During operation, the brushless design of induction motors makes it less likely to have poor contact or spark problems caused by brushes, thereby reducing the failure rate of equipment. The equipment failure rate of induction motors is 30% lower than that of DC motors, especially in situations where long-term stable operation is required.
In extremely high temperature or high humidity environments, brush motors are prone to overheating due to the heat generated by the friction between the brushes and the commutator, while the design of induction motors avoids this problem. For example, in metallurgical plants or ceramic plants, induction motors can operate stably at temperatures above 100°C, while traditional brush motors usually fail in high-temperature environments around 60°C.
In some harsh industrial environments, the brushless characteristics of induction motors reduce the electrical noise and sparks generated by the equipment, reducing the safety risks of operators during work. The accident rate of production lines using induction motors is 25% lower than that of production lines using traditional brush motors.
Underground operations often involve the risk of high concentrations of toxic gases or flammable substances, and any sparks may cause serious accidents. The probability of fire or explosion accidents in mine ventilation systems using induction motors is 40% lower than that of mines using traditional motors. This is particularly important in special environments such as mines and tunnel construction.
The motors in food processing plants often need to work in a clean and waterproof environment, while traditional brush motors are prone to accumulate dust or moisture due to the friction of the brushes, which may cause electrical failures or even fire accidents. The brushless design of induction motors can effectively avoid this situation. In some large meat processing plants, the brushless design of induction motors makes them meet the requirements of the ISO 22000 food safety management system.
High stability
In industrial environments that require long-term and continuous operation, the stability of induction motors is generally better than other types of motors. Especially under long-term operation and high load conditions, the failure rate of induction motors is only 0.2%, which is much lower than the 0.5% to 1% of other motor types.
The stability of induction motors comes from their simplified design and sturdy structure. Compared with DC motors, induction motors do not have complex commutators and brushes. A large metallurgical plant has been operating continuously for more than 15 years in a furnace system driven by induction motors, while other types of motors may need to be replaced many times.
In areas such as mining and heavy machinery, conveyor belt systems using induction motors have a failure rate of only 2% under full load, while conventional motors have a failure rate of up to 8%. The reason for this difference is that induction motors can stably withstand instantaneous load fluctuations and are not prone to failure due to drastic load changes.
In some metallurgical and chemical plants, induction motors often need to operate in high-temperature environments of 60°C to 80°C, and their stability is almost unaffected. Traditional DC motors and synchronous motors usually have a higher failure rate in these environments and require additional cooling systems to maintain stable operation.
In some application scenarios that require large-scale vibration and shock, the design of induction motors enables them to effectively resist external shocks and ensure the operating stability of the equipment under severe vibration. Induction motors can withstand vibrations of up to 20Hz to 100Hz without failure. DC motors and synchronous motors can usually only withstand lower frequency vibrations.
In the event of a short-term overload, induction motors can withstand 120% to 150% of the rated load without thermal damage or failure, while conventional motors can usually only withstand 110% load. In pump and fan systems, induction motors often need to withstand short-term overload conditions, but their stability allows the equipment to continue to operate, reducing the probability of downtime and failure.
Power system instability and voltage fluctuations are common problems in many industrial facilities, but induction motors can operate stably within a voltage fluctuation range of ±10%. In contrast, DC motors and synchronous motors are prone to difficulty starting or shutdown in environments with large voltage fluctuations.
Most induction motors can rely on natural air flow for cooling. In some air conditioning and fan systems, induction motors can remain stable for more than 8 hours of continuous operation without additional forced cooling. Other types of motors may require frequent cooling maintenance and inspections.
In automated production lines in the manufacturing industry, induction motors are widely used in drive systems for equipment such as conveyor belts and robotic arms. The average failure rate of induction motors in automated equipment is only 1%, while the failure rate of DC motors and synchronous motors is 3% to 5%. This gap reflects the high stability of induction motors in integrated systems.