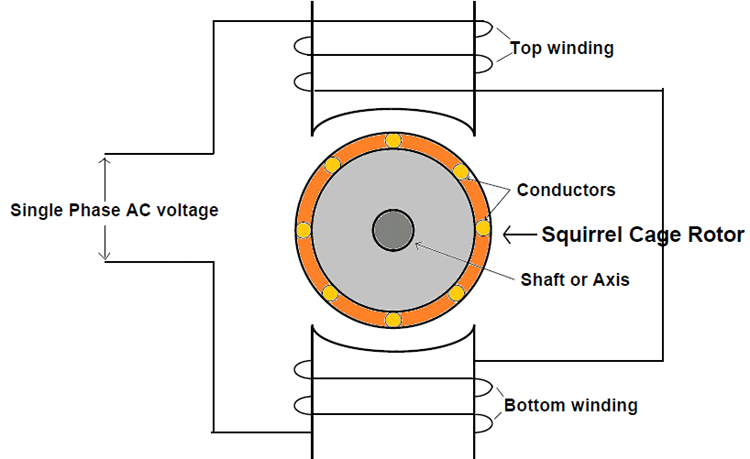
Based on demand, calculate operating environment and usage conditions. Determine the rate of success; demand for the delivery charge is 500 hours, the rate of success is usually 5,000 tiles. Consider factors such as the rate of movement, speed of operation, and the rate of success of the battery.
Table of Contents
ToggleDetermine the Application
A 10 m long automated conveyor must move about 200 kg/min. Assuming the power required for each kg of matter to be moved as 1 W, the power that the motor in the conveyor needs to provide is roughly 200 W. The actual power of the motor selected would be up to about 1 kW.
The fan motor has to run at a lower speed in order to make the operation quiet and stable, mostly within the range of 1000 RPM up to 2000 RPM. For high-speed cutting machines, the speed should be higher, attaining 5000 RPM or even higher. Some precision cutting equipment requires motor speeds of 6000 RPM with power demands around 3 kilowatts.
During starting, a crane may require 3 times the rated torque for short periods. In crane applications, rated power of the motor is around 20 kilowatts, whereas the starting torque may need to exceed 60 kilowatts.
It is estimated that replacing an IE2 motor with an IE3 can save around 10% in energy consumption. Assuming an operation of 8 hours a day for 300 days, using an IE3 motor instead of an IE2 motor could result in an electricity economy of about 5000 yuan.
Generally speaking, a high-load elevator motor has a service life of about 5-8 years while a light-load elevator motor can be over 10 years. In some automated storage systems, motors are required to keep their sizes within 30cm x 30cm with no less than 2 kilowatts power.
If the annual maintenance cost of a motor is 5000 yuan, the total maintenance cost over 5 years may reach 25,000 yuan. Using a more durable, high-quality motor may reduce such costs to 10,000 yuan over 5 years.
Motors used in chemical plants often require protection ratings of IP55 or higher, and in extreme environments, motors may need to meet IP67 protection levels. Motors with PLC control systems in smart manufacturing can achieve higher precision and flexibility without sacrificing power compared to traditional motors.
A regular 2-kilowatt motor would normally cost about 3000 yuan, while its energy-efficient counterpart with the same capacity can reach as high as 4500 yuan. Surveys show that 70% of companies choose brands offering at least a 3-year warranty when purchasing motors.

Calculate the Required Power
In the case of a pump system with a design flow of 50 cubic meters per hour and a head of 30 meters, the generally used required motor power is about 5 kilowatts. In selecting the motor, the fluctuation of the load at startup should be considered, so that the rated power may be selected at 6 kilowatts.
Assuming a fan needs to provide 5000 cubic meters per hour of air volume, with a pressure requirement of 200Pa, based on the fan’s characteristic curve, a 7.5-kilowatt motor may be needed.
The motor’s startup torque must achieve 2.5 times the rated torque in case a crane is carrying a load of 10 tons-or starting power of 30 kilowatts. For this application, the rated power of the motor should be selected at 40 kilowatts to ensure smooth startup with heavy loads.
The power needed from the motor will be around 4 kW if the rated load of the elevator is 1000 kg and rated speed is 1.5 m/sec. On a production line, when the load is 200 kg, for having one operation per minute or 60 operations per hour, usually 3 kW of motor power has to be used in order for continuous, uninterruptive operation to be carried out.
The efficiency of motor cooling is reduced in high-temperature conditions, which may increase power consumption. If the equipment operates in a 40°C environment, the rating of the motor’s power usually needs to be increased by 10%-15%. Therefore, a 10-kilowatt motor may need to be selected as 11.5 kilowatts for high-temperature conditions.
Assume the running time of the conveyor belt is continuous, with a load of 500 kg and a flow rate of 40 tons per hour; the needed power of the motor will be about 5 kilowatts. However, due to the continuous influence that is brought into operation, the increase in selected power of the motor is around 10%-20%. Therefore, in this continuous conveyor, generally, the power chosen for the motor is up to 6 kilowatts for high efficiency during a 24-hour operation.
For instance, for a production line with a rated motor power of 3 kW and with frequent start-stop cycles, the motor power may need to be selected as 4 kW. In some machine shops, one motor has to drive not only the main machine but also additional conveyors and cooling systems. Assuming that the main machine power is 15 kW, the conveyor requires 3 kW and the cooling system requires 2 kW, the total power requirement for the system is 20 kW. A 22-kW motor is normally selected to allow adequate headroom.
Considering an 85% efficiency motor, the other at 90%, though both work with the same load, there will be a difference in power demand and, accordingly, in operating costs. Increasing the efficiency by 5% reduces the active power demand for the same load by approximately 5%.
Consider the Torque Requirements
For a crane with a 10-ton load that needs to start lifting and reach the rated speed within 1 second, the starting torque needs to be 2.5 times the rated torque, or 2500 Nm.
The torque requirement for an electric drill is approximately 40 Nm. For high-performance power tools, torque is typically required between 30-50 Nm. The starting torque for industrial conveyors can be 3 times the rated torque.
Assuming the head of water to be 50 meters and the flow rate 30 cubic meters per hour, the required torque in a water pump system is generally obtained from the work curve of a pump. Assuming a typical water pump system, the required motor torque will be in the order of 100 Nm.
If an elevator has a rated load of 1000 kilograms and a lift height of 30 meters, the torque required by the motor will be proportional to the weight of the load and the distance it is lifted. For some precision milling machines, the variation in the motor’s torque during operation must be less than 5%.
A household washing machine motor uses 500 watts of power, and the torque applied is about 20 Nm whereas for a high-pressure air compressor, the torque applied is normally 500 Nm.
For a high-speed cutting machine, the motor speed may be 10000 RPM with only 10 Nm torque, while in a low-speed heavy-duty extrusion machine, the motor speed is only 1500 RPM but may reach 300 Nm.
In some long-running machinery, the motor torque is lowered with time. For some continuous running rollers, the required motor torque may be reduced from 300 Nm in the beginning to 200 Nm in operation.
Evaluate the Speed Range
For a fan system that has to provide 5000 cubic meters per hour of airflow, for example, considering the design speed is 1500 RPM, the motor speed for this fan is usually chosen within the range of 1500-1800 RPM.
The motor speed usually has to lie in the range of 1000-1500 RPM for a conveyor belt that has a specified speed requirement of 5 meters per minute and a load amounting to 200 kgs.
With large load inertia and the output requirement of 3000 RPM, usually the motor has to run in the range from 0 to 3000 RPM with high starting torque.
It can be assumed that for precision lathes needing to be stable and run slowly, the running range of speeds has to be between 50 RPM and 5000 RPM. High precision lathes may incorporate the use of CNC motors where one can adjust speeds smoothly through the range between 1000 to 5000 rpm.
For an elevator carrying 1000 kilograms at a speed of 1 meter per second, the motor would normally be of the order of 150 RPM. Most motors run between 800 to 1500 RPM. In heavy-duty applications such as mining excavators, the motor typically runs between 500 to 1000 RPM.
In the air conditioning system, a fan motor can be in the range from 500 RPM to 3000 RPM. Assuming an industrial air compressor requires a motor operating at a speed of 1500 RPM and load pressure of 10 bar, the usual range for the motor speed does not exceed 1800 RPM. The usual speed range in which the operation of a motor lies is between 1500 RPM and 1800 RPM.
Given that the speed requirement for cutting wood is around 1000 RPM, and it takes 1500 RPM to cut metals, this category of equipment in principle requires motors whose speed can range within the bracket of 500 to 3000 RPM.

Match the Power Supply Type
In general, the motor power requirement of an industrial fan is 55 kilowatts, and for three-phase AC power supply, the voltage input is generally 400V, with a current requirement of about 100A.
A typical value would be that a given electric tool takes 600 watts with 24 volts DC. In such a case, the kind of current loading may run to approximately 25 amps. The DC supply could be selected concerning continuous load but the startup or inrush currents in the respective device.
For an automated production line, the required current is about 30A at a motor power of 15 kilowatts. The production line motor uses 380V three-phase AC power, and through a variable frequency drive, the motor speed can be changed within the range from 1000 RPM to 3000 RPM.
In the case of huge power equipment like big compressors, the power supply should have a power factor as close to 1 as possible. Assuming that the motor power for a compressor is 100 kW, working voltage is 380V, current is 150 A, the least power factor can be 0.9. Voltage fluctuations must lie within ± 10% limit.
Assuming that a snowmobile uses a 48V battery pack and has a motor power of 2 kilowatts, the capacity of the batteries should not be less than 100Ah.
Assuming that the power of a microscope motor is 100 watts with a voltage of 12V, the required current will be around 8 amps. Equipment usually uses a stable DC power supply with low noise and low fluctuation. A backup generator set uses a diesel engine-driven synchronous generator with a motor power of 500 kilowatts, voltage of 220V/380V.
Determine the Load
The nature and size of the load to be driven must be clearly identified in addition to the type of the load and how it impacts motor operation. Now, for this small fan, assume that the blade diameter is 1 meter and air resistance during rotation is 10 N, so the motor must be able to provide the torque equivalent to overcome this 10 N resistance. If the fan operates at 1500 RPM, generally the power required in the motor lies between 50 watts to 200 watts.
In a conveyor with a given load of 500 kilograms, the speed can be set as 5 meters per minute; for such applications, a typical motor size chosen would be around 2-kilowatt, about 4A, with speed set via a variable frequency drive.
That is to say, if a crane lifts a 10-ton load at a speed of 3 meters per minute, the motor power needed is approximately 15 kW, with a current load of about 30A.
An electric drill working with hard materials can face a double or triple increase in load. Here, the normal load of the drill is 200 watts, but when the load is increased, up to 400 watts of power are demanded from the motor. When selecting a motor, attention should be paid to its power margin: at least 1.5 times higher than the rated power is chosen.
Substituting the values, when the gearbox requires 100Nm of torque at a speed of 1500 RPM, using the formula for calculation of power, P = 2πNT/60, the required power that has to be provided by a motor to provide 100Nm of torque at 1500 RPM is 2.62 kilowatts.
If the starting load of a water pump is supposed to be 2 times of a normal load, a highly instantaneous torque requires, for example, a 10-kilowatt motor; simultaneously, because of high starting torque, rated power of 1.5 times is needed.
An industrial mixer may experience a load increase of 2 to 3 times when mixing heavier materials. If the standard power requirement is 1 kilowatt, the motor may need 3 kilowatts when mixing heavy materials.
A cooling pump may have a normal load of 10 kilowatts but increases at high temperatures to 15 kilowatts. If the flow rate through such a pump is 10 cubic meters per hour during normal conditions, it may be reduced to 7 cubic meters per hour in high load situations.
A fan motor operating under high-temperature conditions may be forced to operate with temperatures as high as 80°C. With a normal operating load of 500 watts on the fan, under high-temperature conditions, its effective power output on the motor falls to 400 watts.
Check the Installation Space
Suppose you are selecting a motor for a machine tool whose installation space is 300mm × 300mm × 400mm, while the dimensions of the selected motor are 250mm × 250mm × 350mm. In such selection, enough space must be allowed for entry of cables and installation of other accessories for normal operation.
In case the motor selection is for a large electric pump with 75 kilowatts power and 1500 RPM, there should be at least 30% space left around the motor for ventilation and cooling.
A motor that has a pulley might have a shaft that is 10 to 15 centimeters longer compared with a direct-drive motor. There must be enough room in the installation site for the entire motor and the pulley system.
When choosing a motor, it is worth considering special attention to be paid to position and connection method of the motor terminals for easy and quick installation of all wirings.
Motors operating in extreme conditions like high temperatures, high humidity, or corrosive gas require room for installation to fasten the protective cover and seal devices for the prevention of external environmental impacts on the motor. In the selection of the motor, besides consideration of the size, the convenience of long-term maintenance should be considered.