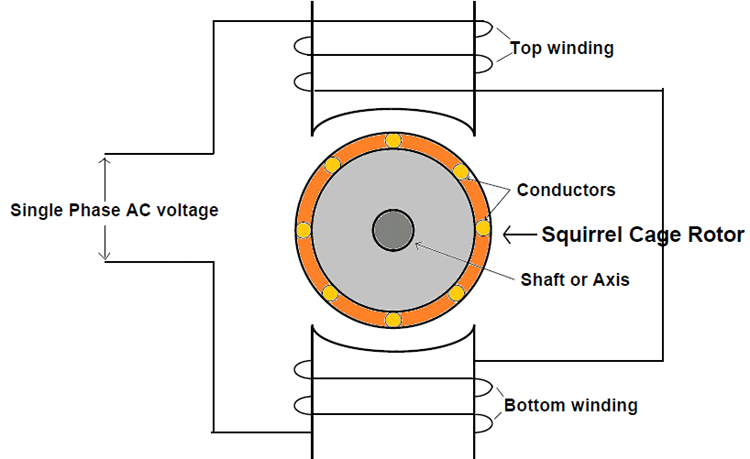
Three-phase squirrel-cage induction motors account for 70-80% of the global industrial motor usage. They are chosen for their ruggedness, high efficiency (85-95%), and low maintenance. They are usually around 85-95% efficient at load, meeting international standards such as IEC 60034-30-1 (IE3/IE4 efficiency classes).

Table of Contents
ToggleDC Motors
The global DC motor market reached approximately $8.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6% through 2030.
Currently, 70% of global electric vehicles utilize DC motors. A standard electric vehicle typically employs DC motors with power ratings ranging from 20 kW to 200 kW, achieving energy efficiency exceeding 90%. Over 60% of global automated production equipment relies on DC motors.
DC motors are widely used in frequency conversion control systems for wind turbines, where their conversion efficiency often exceeds 95%. In the printing industry, DC motor-equipped devices achieve speed regulation accuracy within 0.1%.
The brushes in a standard DC motor typically require replacement every 1,000 hours, translating to 2–3 replacements annually. Brush replacement costs account for roughly 30% of total DC motor maintenance expenses.
Brushless DC motors (BLDC) are generally 20% more efficient than brushed motors, with lifespans exceeding 10,000 hours, compared to approximately 2,000–3,000 hours for brushed motors.
Around 25% of electrical equipment employs DC motors for power conversion and regulation, with conversion losses limited to under 5%. Globally, 50% of household appliances and 30% of industrial robots use DC motors. High-precision robots typically utilize DC motors with power outputs between 0.5 kW and 5 kW.
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM)
The global market value of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM) reached billion by 2030, with an annual growth rate of 6.5%.
Approximately 80% of global electric vehicles utilize PMSMs. These motors typically have a power range from 30 kW to 300 kW in electric vehicles, maintaining an energy efficiency of over 90%. For instance, the efficiency of a drive motor in a medium-sized electric vehicle can reach 92%, whereas traditional induction motors usually operate at around 85%.
About 60% of robots worldwide use PMSMs. In robotic arms, PMSMs can provide up to three times the torque density of conventional motors.
PMSMs have captured about 50% of the global market share in wind turbine generators. The latest generation of 5 MW wind turbine generators, which use PMSMs, can achieve efficiencies of over 96% and have an operational lifespan of up to 25 years.
The power density of PMSMs is typically 2 to 3 times that of traditional motors. Some small aircraft and drones have started using PMSMs, with power densities reaching 4 kW per kilogram. The application rate of PMSMs in equipment such as cranes and conveyor belts is approaching 50%.
The initial investment cost of PMSMs is generally 30% to 50% higher than that of induction motors, but prices are expected to decrease by 20% to 30% in the coming years.
The latest generation of high-performance inverters can increase the speed regulation range of PMSMs from the original 1000 rpm to 5000 rpm.
Stepper Motors
The global market size of stepper motors reached billion by 2030, with an annual growth rate of 5.5%.
Approximately 60% of automated production line equipment worldwide uses stepper motors. Stepper motors ensure that each workpiece is assembled at precise intervals, with errors typically controlled within 0.1 millimeters.
About 40% of global CNC machine tools are equipped with stepper motors. Around 70% of 3D printers worldwide use stepper motors as their core driving units. A commercial 3D printer can achieve a positioning accuracy of 0.01 millimeters.
Approximately 50% of medical devices globally use stepper motors, and about 30% of high-end household appliances employ stepper motors as their driving mechanisms. However, stepper motors may experience vibration and noise issues during low-speed operation.
Compared to servo motors, stepper motors are typically 40% to 50% cheaper. The positioning accuracy of stepper motors can range between 1.8 degrees and 0.9 degrees.
Servo Motors
The global servo motor market reached billion by 2030, with an annual growth rate of approximately 5.2%.
About 80% of high-end automated equipment utilizes servo motors. Around 70% of industrial robots use servo motors. Approximately 40% of aerospace equipment employs servo motors, and about 30% of electric vehicles use servo motors as part of their driving systems.
Compared to standard motors, servo motors are typically 20% to 30% more efficient. Production lines using servo motors can reduce overall energy consumption by 15% to 25%.
Servo motors equipped with intelligent control systems have a response speed that is 30% faster than traditional servo motors. About 60% of high-end precision machining equipment uses servo motors.
The initial investment cost of servo motors is usually 40% to 50% higher than that of standard motors, but prices are expected to decrease by 20% to 30% in the coming years. The average lifespan of servo motors can exceed 100,000 hours.
Explosion-Proof Motors
The global market size of explosion-proof motors reached billion by 2030, with an annual growth rate of approximately 7.5%.
Around 60% of global oil and gas extraction equipment is equipped with explosion-proof motors. An explosion-proof motor used in oil drilling typically has a rated power ranging from 75 kW to 250 kW.
Approximately 40% of chemical plants worldwide use explosion-proof motors to drive equipment, about 50% of mining operations utilize explosion-proof motors, and around 35% of pharmaceutical factories employ explosion-proof motors.
In large-scale mining equipment, the power of explosion-proof motors can reach 500 kW or even higher. On oil drilling platforms, explosion-proof motor-driven fans and pumps can provide power exceeding 200 kW.
The failure rate of explosion-proof motors is typically below 1%. In industries requiring 24/7 uninterrupted operation, explosion-proof motors have become an ideal choice.
Brushless Motors vs. Brushed Motors
The global brushless motor market reached billion by 2030, with an annual growth rate of 8.5%. Compared to brushed motors, brushless motors are typically 20% to 30% more efficient.
The average lifespan of brushless motors can exceed 10,000 hours, while brushed motors usually have a lifespan of only 2,000 to 3,000 hours.
Approximately 60% of low-power household appliances use brushed motors. In some traditional power tools and household appliances, brushed motors still hold about 30% of the market share.
Brushed motors tend to generate significant heat under high load or prolonged operation.
Around 40% of global high-precision instruments use brushless motors.
In electric vehicle drive systems, brushless motors can achieve a maximum power of over 300 kW.
Synchronous Motors vs. Asynchronous Motors
The global synchronous motor market size was billion by 2030, with an annual growth rate of approximately 6%. Asynchronous motors account for about 60% of the global motor market.
The main speed of synchronous motors is strictly synchronized with the grid frequency, enabling them to provide highly precise speed control.
The purchase and maintenance costs of synchronous motors are approximately twice those of asynchronous motors. In a typical chemical plant, using synchronous motors to drive compressors can save about 10% to 15% in annual power consumption.
Around 70% of global industrial motors are asynchronous motors. In an ordinary pumping station, the power of asynchronous motors typically ranges from 5 kW to 100 kW.
The mean time between failures (MTBF) of asynchronous motors can exceed 15,000 hours. Asynchronous motor-driven conveyor belts can operate 24/7 with an annual failure rate of less than 1%.
The control accuracy of synchronous motors can typically reach within 0.1%. The speed fluctuation of asynchronous motors is usually within 5%. Asynchronous motor-driven fans typically have a power range of 50 kW to 500 kW.