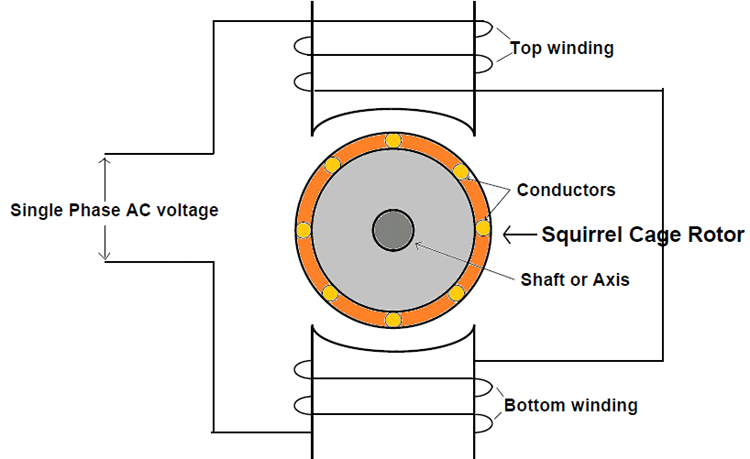
You can check the voltage type on the name plate. The common marking for DC motors is the DC voltages such as 12V, 24V, etc., whereas AC motors bear the marking for AC voltages such as 220V, 380V, etc. Commonly, AC motors are also marked for frequency of either 50Hz or 60Hz.
Table of Contents
TogglePower Input Types
This accordingly sets a common working voltages for most DC motors to be within approximately 12 to 48 V—being small devices. Commonly, using a typical power tool, like an electric drill that uses a 24V electric battery, while the power has a range from 200W up to 500W. Using these from the DC power interface on a device, after indicating the voltage ranges within 12 to 48 V, you should clarify what has been said; it is obviously a DC motor.
The general household or industrial AC power sources are 220V or 380V. The power of a common household air conditioner might be from 1.5 kW to 3 kW, the input voltage for the motor is 220V, and the frequency is 50Hz.
The point to note here is that DC motors use batteries or specific adapters for the current supply, while AC motors can be powered directly from a household outlet or any industrial power supply. For example, an electric washing machine would need an AC motor with ratings of 300W to 500W at an input voltage of 220V and a frequency of 50Hz, hence suitable for a household 220V power system.
DC motors are able to control their speed by adjusting the input voltage. A typical electric shaver has a power of 10W, with a battery voltage of 3.7V, and can run for about 30 minutes to 1 hour. When the voltage drops, the speed also decreases.
The efficiency of DC motors used in power tools can be as high as 70% to 90%. For instance, a battery-powered power tool equipped with a DC motor has a full-load power of 300W, a battery voltage of 18V, and a battery capacity of 2000mAh, which can sustain the tool operating for about 30 minutes to 1 hour after a full charge.
The power rating of industrial motors ranges from 10kW to several hundred kW, with 380V three-phase AC. For example, the heavy machinery motor in a factory could have the following parameters: power 50kW, voltage 380V, frequency 50Hz, and speed 3000 rpm. The power of the pump motor of a household water heater is usually between 100W and 200W, the input voltage is 220V, and the frequency is 50Hz.

Check Nameplate Information
In cases where the rated voltage on the nameplate is DC voltage, such as 12V, 24V, 48V, etc., then it is a DC motor. For example, in every ordinary 12V DC motor, the nameplate marks “12V DC” and the power is between 20W to 100W. If the voltage marked on the nameplate is 220V, 380V, etc., then the motor is an AC motor.
The nameplate of the AC motor gives the frequency—50Hz or 60Hz. For example, the standard frequency of China is 50Hz while in the United States it is a 60Hz power system.
The power range of AC motors is from several watts up to hundreds of kilowatts. For example, the power of a household electric fan is between 60W and 150W, and the nameplate might show “220V AC, 50Hz, 60W”. DC motors usually do not exceed 500W in power. A 12V DC motor with a power of 200W will have a nameplate reading “12V DC, 200W”.
A 12V DC motor can take in currents from 10A to 20A. In most of the small power tools and household appliances, it does not exceed 5A. For example, a 250W AC motor can take in around 1.1A and a 1kW AC motor takes in about 4.5A.
The nameplate of power tools often indicates the speed range, such as “3000RPM-6000RPM”. Typically, a 50Hz AC motor runs at 1500 rpm, while a 60Hz motor runs at 1800 rpm. If the nameplate indicates “3000RPM” without specifying speed control, it can be determined that it is an AC motor.
Some DC motors are labelled as “DC Brushless” or “DC Brushed” on the nameplate. If the nameplate reads “AC Induction” or “AC Synchronous”, this is an AC induction motor or synchronous motor. As an example, the nameplate of the industrial motor may read “380V AC, 50Hz, 15kW”, and the power is several tens of kilowatts.
The level of efficiency of modern industrial motors is usually indicated by IE, International Efficiency. The IE3 motors can achieve efficiency over 90%, while the IE2 motors typically have an efficiency of about 85%.
Brushes and Commutators
DC motors usually have brushes and a commutator, while AC motors do not. The most common DC motors used, such as the 12V and 24V small power tools, are the ones with brushes and a commutator to keep the current direction constant in rotation. A normal 12V DC motor is drawing a current of 5A to 10A, and thus the power has about 60W to 100W. The life of the brushes is usually within the range from 1000 hours up to 2000 hours.
A 500W household fan AC motor, whose power may be in the range of 50W to 150W, has a current of 0.5A to 1.0A, rated voltage of 220V, and working frequency of 50Hz. Since the direction of current naturally changes, maintenance cost is a little lower during normal use.
A high-efficiency industrial AC motor with a power of 15kW, an input voltage of 380V, a frequency of 50Hz, and a current of 30A to 40A can operate for thousands of hours at high load without needing to replace brushes.
A 24V rated voltage, 300W, 12A current DC motor in a power tool would need to replace brushes and commutator after several hundred hours of running. Large DC motor brushes can be designed to last as long as 5000 hours. A 500W rated power, 24V rated voltage, 20A current brushless DC motor normally has an efficiency over 85% and its lifetime is usually over 5000 hours.
The variable frequency air conditioner motor has the power of 1.5kW, 6A of current, and voltage of 220V at 50Hz. It uses a brushless induction motor. The inverter controls the change in frequency for fine temperature control with low energy consumption.
Brushes for DC motors may be replaced after 1000-2000 hours of work. In AC motors, repairs are needed only in cases of motor damage.
Measure Operating Frequency
The operating frequency of AC power systems in most countries around the world is either 50Hz or 60Hz. The standard frequency is 50Hz in China and 60Hz in the United States and some other countries. If the display of a frequency measuring device indicates that the working frequency of a motor is at 50Hz or 60Hz, then it will be an AC motor. Such as the industrial 5kW AC motor, which will maintain a working frequency of 50Hz during operation.
A normal running and typical 12V DC motor will display a frequency close to zero on a frequency measuring device. The AC motor in the air conditioner will have a frequency converter to regulate the frequency due to indoor temperature fluctuations. If an air conditioner motor with rated power 2kW takes a current of 10A at a voltage of 220V, the frequency might adjust to 60Hz under high load and 50Hz under low load.
If the frequency measured from the motor is 50Hz and the speed is synchronized with the power frequency, it can be confirmed to be synchronous motors. Example: A 220V AC motor operates at a speed of 1500 rpm at 50Hz frequency.
Operating frequency in DC motors would always be zero or near to zero even when they are supplied using variable frequency drive and other frequency-based controls. The point is clarified further, a DC motor of capacity 500 watt drawing 20amp on 24V will develop an operating frequency as zero or minimum.
Induction motors are normally connected directly to the mains where the operating frequency is either 50Hz or 60Hz. The speed of a BLDC is generally changed by an electronic controller. If the frequency measured happens to be 0 and the motor has precision in speed, then it must be a brushless DC motor.
Such as, the rated current of the 5kW AC motor is 20A, the voltage is 380V, the working frequency is 50Hz, and there is abnormal frequency fluctuation during use, indicating that the power supply or motor itself may not be stable.
Motor Wiring Methods
A common 24V DC motor has two input wires which connect with the positive and negative terminals of the battery or power supply. The input wires for a 500W household fan motor that requires an input power supply of 220V AC is three in number.
One simple application can have a 15kW three-phase, three wiring inlet power lines connected with a three-phase power source. Wiring of the air conditioner variable-frequency motor includes three AC power lines and a lot of lines that allow control of that motor. In principle, an Electronic controller comes with each BLDC Motor. Such that: A 24V BLDC motor has not only two basic power lines, it also has Control signal lines.
The motor also would have a number of power lines, ground lines, and many lines of control signals. All these extra terminals are used by users for controlling the motor.
In a big fan AC motor, there would be several input ports and several control ports that depend on the operation state of the motor. In the DC motor, usually, the wiring terminals are pretty simple and require a DC power supply.
Detect Voltage Waveforms
The voltage waveform of a DC motor is stable and linear. For example, the input voltage waveform of a 24V DC motor will be a straight line, which stays close to 24V.
The voltage waveform of an AC motor has periodic fluctuations. For example, the input voltage waveform of a 220V single-phase AC motor will approximately show a 60Hz sine wave. In China’s standard power grid, the frequency is 50Hz, and the voltage waveform alternates 50 times per second.
Three-phase AC power includes three sine waves that are 120 degrees apart from each other in phase. The waveform of input voltage for the 380V three-phase AC motor would include three sine waves, each 120 degrees apart.
A 5kW AC motor, for example, could be inverter-driven: at low load, the waveform can be square or triangular, and at high load, it shifts to a sine wave. Voltage waveforms for a 48V brushless DC motor will show high-frequency pulse waves; the amplitude and frequency of the waveform depend upon the PWM signal from the controller.
The voltage waveform for a normally operating AC should be a sine waveform. Any abnormal spikes or distortion in the waveform may indicate a short circuit in the motor windings or an unstable power supply.
Determine Starting Methods
Common direct-current motors, such as small 12V or 24V motors, all use direct connect to the power at startup. For instance, a 24V DC motor will have directly applied 24V at its startup, while the starting current will be 5-8 times the rated working current. If the rated current of a motor is 2A, it may rise up to about 10A while it starts.
AC motors often use several starting methods for the purpose of starting current limitation. The common ways of starting an AC motor include star-delta starting, soft starting, and variable frequency starting.
When the motor starts with star-delta starting, the current is reduced to one-third of the normal operating current. Once the motor reaches a certain speed, the wiring method switches to a delta connection for normal operation. For example, a 7.5kW three-phase motor starting with a star-delta method will reduce the starting current from 50A to around 16A.
Soft starting for a 15kW AC motor would bring the starting current down to 1.5 to 2 times the rated current. A 10kW motor driven by a frequency converter can increase the voltage from zero gradually and adjust the frequency in real time based on the load condition.
A 24V brushless DC motor normally uses a PWM signal to control the starting current. In case of proper design of the electronic controller, the starting current will not be more than double the rated current. The method of gradual increase of voltage at startup may be used for big power tools using DC motors in order to reduce the impact on the battery or power supply.